Abstract
Research Article
Innovative results in the treatment of inespecific anusitis-proctitis with the use of bergamot gel (Benebeo gel)®
Danilo Cafaro, Felipe Celedon, Alessandro Sturiale and Maria Stefania Sinicropi*
Published: 27 November, 2019 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 020-024
Inflammation is a complex biological reaction induced by the alteration of tissue homeostasis, which occurs in response to the presence of a biological, chemical or physical agent in the body [1]. The acute inflammatory response is composed of an elaborate cascade of both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators, and balance between these mediators often determines the outcome after injury [2]. Generally during acute inflammation, cellular and molecular events and interactions reduce the risk of eventual injuries or infections. However, acute inflammation can become chronic, contributing to a variety of chronic inflammatory diseases [3]. Major micro circulatory events that occur during the inflammatory process include changes in vascular permeability, leukocyte recruitment and accumulation, and inflammatory mediator’s release [4].
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001011 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Maskrey BH, Megson IL, Whitfield PD, Rossi AG. Mechanisms of resolution of inflammation: a focus on cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011; 31: 1001-1006. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21508346
- Ward PA, Lentsch AB. The acute inflammatory response and its regulation. Arch Surg. 1999; 134: 666-669. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10367878
- Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget. 2017; 9: 7204-7218. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29467962
- Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE. Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007; 147: 227-235. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17223962
- Kriplani P, Guarve K, Baghel US. Novel Herbal Topical Patch containing Curcumin and Arnica Montana for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2019. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30767746
- Miller AD, Ly BT, Clark RF. Neonatal hemolysis associated with nursing mother ingestion of arnica tea. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009; 47: 726.
- Spigoni V, Mena P, Fantuzzi F, Tassotti M, Brighenti F, et al. Bioavailability of Bergamot (Citrus bergamia) Flavanones and Biological Activity of Their Circulating Metabolites in Human Pro-Angiogenic Cells. Nutrients. 2017; 9: 12. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29211032
- Formisano C, Rigano D, Lopatriello A, Sirignano C, Ramaschi G, et al. Detailed Phytochemical Characterization of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) by UPLC-DAD-MS and LC-NMR. J Agric Food Chem. 2019; 67: 11. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30807134
- Penninger JL, Zainea GG. Common anorectal conditions: Part II. Lesions. Am Fam Physician. 2001; 64: 77-88. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11456437
- Dawson H, Serra S. Tumours and inflammatory lesions of the anal canal and perianal skin revisited: an update and practical approach. Journal of Clinical Pathology; 68: 971-981. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26602415
- Gattuso G, Caristi C, Gargiulli C, Bellocco E, Toscano G, et al. Flavonoid glycosides in bergamot juice (Citrus bergamia Risso). J Agric Food Chem. 2006; 54: 3929-3935. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16719517
- Dugo P, Presti ML, Ohman M, Fazio A, Dugo G, et al. Determination of flavonoids in citrus juices by micro-HPLC-ESI/MS. J Sep Sci. 2005; 28: 1149-1156. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16116991
- Corasaniti MT, Maiuolo J, Maida S, Fratto V, Navarra M, et al. Cell signaling pathways in the mechanisms of neuroprotection afforded by bergamot essential oil against NMDA-induced cell death in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 2007; 151: 518-529. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17401440
- Navarra M, Femia AP, Romagnoli A, Tortora K, Luceri C, et al. A flavonoid-rich extract from bergamot juice prevents carcinogenesis in a genetic model of colorectal cancer, the Pirc rat (F344/NTac-Apcam1137). Eur J Nutr. 2019. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30919084
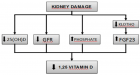
- La Russa D, Giordano F, Marrone A, Parafati M, Janda E, et al. Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019; 8. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30884780
- Perna S, Spadaccini D, Botteri L, Girometta C, Riva A, et al. Efficacy of bergamot: From anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms to clinical applications as preventive agent for cardiovascular morbidity, skin diseases, and mood alterations. Food Sci Nutr. 2019; 7: 369-384. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30847114
- Mirielle CN, Jeremy JJ. Clinical application of bergamot (Citrus bergamia) for reducing high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease markers. Integr Food Nutr Metab. 2019. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31057945
- Parafati M, Lascala A, La Russa D, Mignogna C, Trimboli F, et al. Bergamot Polyphenols Boost Therapeutic Effects of the Diet on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Induced by "Junk Food": Evidence for Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Nutrients. 2018; 10. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30388763
- Daniela I, Marika C, Michela C, Enrico G, Emanuela E, et al. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Flavonoid-Rich Fraction of Bergamot Juice (BJe) in a Mouse Model of Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Pharmacol. 2016; 7: 203. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27471464
- Impellizzeri D, Bruschetta G, Di Paola R, Ahmad A, Campolo M, et al. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of bergamot juice extract (BJe) in an experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Nutr. 2015; 34: 1146-1154. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25491246
- Man MQ, Yang B, Elias PM. Benefits of Hesperidin for Cutaneous Functions. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019; 2019: 2676307. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31061668
- Risitano R, Currò M, Cirmi S, Ferlazzo N, Campiglia P, et al. Flavonoid fraction of Bergamot juice reduces LPS-induced inflammatory response through SIRT1-mediated NF-κB inhibition in THP-1 monocytes. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e107431. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25260046
- Lorzadeh E, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Mohammadi M, Khoshbakht Y, Salehi-Abargouei A. The effect of hesperidin supplementation on inflammatory markers in human adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Chem Biol Interact. 2019; 307: 8-15. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30991044
- Nisticò S, Ehrlich J, Gliozzi M, Maiuolo J, Del Duca E, et al. Telomere And Telomerase Modulation By Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction In Experimental Photoageing In Human Keratinocytes. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2015; 29: 723-728. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26403416
- Ittiudomrak T, Puthong S, Roytrakul S, Chanchao C. 15α-Mangostin and Apigenin Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Programmed Cell Death in SKOV-3 Ovarian Cancer Cells. Toxicol Res. 2019; 35: 167-179. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31015899
- Graziano AC, Cardile V, Crascì L, Caggia S, Dugo P, et al. Protective effects of an extract from Citrus bergamia against inflammatory injury in interferon-γ and histamine exposed human keratinocytes. Life Sci. 2012; 90: 968-974. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22634580
- Hiramitsu M, Shimada Y, Kuroyanagi J, Inoue T, Katagiri T, et al. Eriocitrin ameliorates diet-induced hepatic steatosis with activation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Sci Rep. 2014; 4: 3708. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24424211
- Miyake Y. Lemon flavonoid, eriocitrin, suppresses exercise-induced oxidative damage in rat liver. Life Sciences.
- Bruno A, Pandolfo G, Crucitti M, Cedro C, Zoccali RA, et al. Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction Supplementation Improves Cognitive Functioning in Schizophrenia: Data From an 8-Week, Open-Label Pilot Study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2017; 37: 468-471. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28591067
- Rombolà L, Tridico L, Scuteri D, Sakurada T, Sakurada S, et al. Bergamot Essential Oil Attenuates Anxiety-Like Behaviour in Rats. Molecules. 2017; 11: 22. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28398260
- Navarra M, Ferlazzo N, Cirmi S, Trapasso E, Bramanti P, et al. Effects of bergamot essential oil and its extractive fractions on SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell growth. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015; 67: 1042-1053. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25808679
- Celia C, Trapasso E, Locatelli M, Navarra M, Ventura CA, et al. Anticancer activity of liposomal bergamot essential oil (BEO) on human neuroblastoma cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24099646
- Danilo Cafaro; Maria Stefania Sinicropi. Creation and experimentation of mesalazine gel and bergamot flavonoid fraction (Benebeogel®) for the treatment ofnon-specific proctitis. Tech Coloproctol. 2018.
- Cafaro D, Sturiale A, Fortuna V, Sinicropi MS, Naldini G. Clinical effect of the bergamot-derived gel (Benebeo gel®)associated with mesalazine for the treatment of anitis and proctitis. Trend Gen Pract. 2018; 2.
- Shanley TP, Foreback JL, Remick DG, Ulich TR, Kunkel SL, et al. Regulatory effects of interleukin-6 in immunoglobulin G immune complex-induced lung injury. Am J Pathol. 1997; 151: 193- 203. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9212745
- Castellani P, Balza E, Rubartelli A. Inflammation, DAMPs, Tumor Development, and Progression: A Vicious Circle Orchestrated by Redox Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014; 20: 1086–1097. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23373831
- Tabas I, Glass CK. Anti-inflammatory therapy in chronic disease: Challenges and opportunities. Science. 2013, 339: 166–172. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23307734
- Oliveira-Marques V, Marinho HS, Cyrne L, Antunes F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in NF-kappaB. Activation: From inducer to modulator. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2223–2243. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19496701
- Vollgraf, U, Wegner M, Richter-Landsberg C. Activation of AP-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB transcription factors is involved in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptotic cell death of oligodendrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1999; 73: 2501-2509. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10582611
Figures:

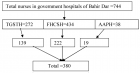
Figure 1
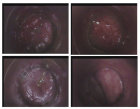
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Dendritic cells and TNF-Related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) represent new possibilities for sepsis treatmentPetya Ganova,Lyudmila Belenska-Todorova,Nina Ivanovska*. Dendritic cells and TNF-Related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) represent new possibilities for sepsis treatment. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hcci.1001001; 1: 001-004
-
Brain response in some systemic immune condition-Toxicological aspectsLuisetto M*. Brain response in some systemic immune condition-Toxicological aspects. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001002; 1: 005-008
-
The Immunitary role in chronic prostatitis and growth factors as promoter of BPHMauro luisetto*,Behzad Nili-Ahmadabadi,Ghulam Rasool Mashori,Ram Kumar Sahu,Farhan Ahmad Khan,Cabianca luca,Heba Nasser. The Immunitary role in chronic prostatitis and growth factors as promoter of BPH. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001003; 2: 001-013
-
Expression of C-type Natriuretic Peptide and its Specific Guanylyl Cyclase-Coupled Receptor in Pig Ovarian Granulosa CellsSoo Mi Kim,Suhn Hee Kim,Kyung Woo Cho,Sun Young Kim,Sung Zoo Kim*. Expression of C-type Natriuretic Peptide and its Specific Guanylyl Cyclase-Coupled Receptor in Pig Ovarian Granulosa Cells. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001004; 2: 014-025
-
Endogenous Ligands of Toll Like Receptors: A Danger Signal to the Brain Memory at High AltitudeKP Mishra*,Shashi Bala Singh. Endogenous Ligands of Toll Like Receptors: A Danger Signal to the Brain Memory at High Altitude. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001005; 2: 026-027
-
Differentiation of bone marrow cells in arthritic mice with decreased complement activityPetya Ganova,Nina Ivanovska*. Differentiation of bone marrow cells in arthritic mice with decreased complement activity. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001006; 2: 028-038
-
Effect of common food additives on mast cell activationCarena MP,Mariani ML,Ordóñez A,Penissi AB*. Effect of common food additives on mast cell activation. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001007; 3: 001-005
-
Association of Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 gene polymorphism with high altitude induced thrombosis patients in Indian populationSwati Sharma,Iti Garg*,Gauri Mishra,Babita Kumari,Lilly Ganju,Bhuvnesh Kumar. Association of Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 gene polymorphism with high altitude induced thrombosis patients in Indian population. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001008; 3: 006-015
-
Altitude sickness and Antarctic polar plateau: A reviewKP Mishra*,Shashi Bala Singh. Altitude sickness and Antarctic polar plateau: A review. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001009; 3: 016-018
-
Proposal for the elimination of allergiesJames F Walles*. Proposal for the elimination of allergies. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001010; 3: 019-019
Recently Viewed
-
Relationship between Vitamin D Deficiency and Lipopolysaccharides Porphyromonas gingivalis Bacteria in Stunting ChildrenErwin Gunawan*,Ria Puspitawati. Relationship between Vitamin D Deficiency and Lipopolysaccharides Porphyromonas gingivalis Bacteria in Stunting Children. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001033; 8: 059-065
-
Addiction to self-strangulation: a case-reportAurely Ameller*,Yann Le Strat,Marion Cadranel,Celine Portalier, Caroline Dubertret. Addiction to self-strangulation: a case-report . J Addict Ther Res. 2017: doi: 10.29328/journal.jatr.1001003; 1: 016-021
-
Nanoencapsulated Extracts from Leaves of Bauhinia forficata Link: In vitro Antioxidant, Toxicogenetic, and Hypoglycemic Activity Effects in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic MiceBárbara Verônica Cardoso de Souza, Alessandra Braga Ribeiro*, Rita de Cássia Meneses Oliveira, Julianne Viana Freire Portela, Ana Amélia de Carvalho Melo Cavalcante, Esmeralda Maria Lustosa Barros, Luís Felipe Lima Matos, Tarsia Giabardo Alves, Maria. Nanoencapsulated Extracts from Leaves of Bauhinia forficata Link: In vitro Antioxidant, Toxicogenetic, and Hypoglycemic Activity Effects in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Mice. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001063; 8: 100-115
-
Oral Suspension as Versatile Galenic Formulation in PediatryMauro Luisetto*, Almukthar N, Edbey K, Mashori GR, Fiazza C, Dona’ l, Cabianca L, Latyshev O. Oral Suspension as Versatile Galenic Formulation in Pediatry. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001062; 8: 091-099
-
Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on DepressionKousik Maparu*. Modulation of Microbiota and its Impact on Depression. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001061; 8: 089-090
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."